What is Exercise Therapy?
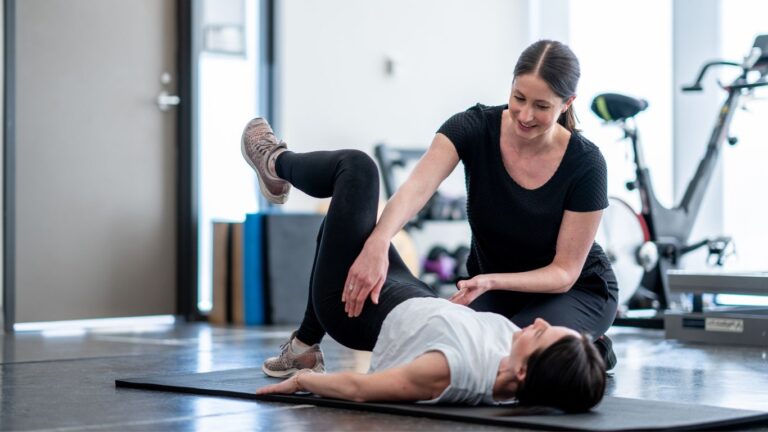
Exercise therapy is a form of physical treatment with a focus on the structured and strategic movement of the body to aid in recovery and enhance overall health. You might consider it if you’re recovering from an injury or suffering from certain chronic conditions. By engaging in targeted exercises, your body can work to restore function, relieve symptoms, increase mobility, and improve fitness levels. At its core, it’s about using exercise as medicine, applying it methodically to address specific health needs and goals.
The benefits of exercise are extensive and well-supported by scientific evidence. Through consistent therapeutic exercise, you stand to gain improved strength, better balance, enhanced flexibility, and reduced risk of chronic disease. Whether you’re looking to bounce back after an injury or simply want to maintain a level of physical wellness, exercise therapy can be tailored to your individual situation, aiming to maximize your participation in daily life.
Your journey with exercise therapy may begin with an assessment by a healthcare professional who can prescribe the right set of exercises for your unique health scenario. These exercises are not just a random set of movements; they’re carefully designed to improve different parts of your body’s function. For example, they may focus on areas like strength building for weakened muscles, enhancing mobility in stiff joints, or correcting movement patterns to prevent future injuries. Each exercise is a step towards a more active and capable you, letting you take control of your health and recovery process.
Understanding Exercise Therapy
When you hear “exercise therapy,” think targeted movements designed to heal and enhance your body’s function. It’s about more than just getting fit; it’s a tailored approach to improve your health and mobility through specific exercises.
Defining Exercise Therapy
Exercise therapy employs carefully selected physical activities to support rehabilitation and contribute to your overall wellness. Unlike general exercise, it consists of personalized exercise interventions that medical professionals use in clinical practice to address specific health issues. It’s a structured process where treatment goes hand-in-hand with movement to boost your body’s ability to function optimally.
Exercise Therapy vs. Physical Therapy
While both exercise therapy and physical therapy share the goal of rehabilitating your body, they aren’t identical. Exercise therapy is a subset of physical therapy that concentrates specifically on physical activity to aid recovery. Meanwhile, physiotherapy is broader, encompassing various techniques, of which exercise is just one. It includes hands-on manipulation and the use of equipment to treat a wide range of injuries and conditions.
In essence, exercise therapy zeroes in on the therapeutic aspect of movement within the larger umbrella of physical therapy, illustrating its key role in your recovery and long-term health.
Components of Exercise Therapy
Exercise therapy encompasses a wide range of activities designed to improve your health and physical well-being through structured and systematic movement. At the heart of this therapy are individualized exercise programs and a variety of therapeutic exercises aimed at enhancing physical function.
Exercise Programs and Prescription
Your exercise therapy journey often starts with a tailored exercise prescription. This plan is predicated on the FITT principle – Frequency, Intensity, Time, and Type – to match your specific health needs and fitness goals. An effective exercise program balances aerobic exercise to improve your cardiovascular health and resistance training to build strength. Over time, the intensity and resistance are adjusted to continually challenge your body and promote strength and endurance.
Types of Therapeutic Exercises
Therapeutic exercises can be divided into several categories:
- Strengthening exercises: These exercises are designed to increase muscle power, endurance, and size. They typically involve using a form of resistance with varying sets, repetitions, and velocities, dependent on desired outcome.
- Flexibility exercises: Such exercises aim to improve your mobility and flexibility, essential for maintaining your range of motion and preventing injuries.
- Coordination exercises: To enhance your movement patterns and coordination, these exercises can help in refining your motor skills, so your body moves more efficiently.
A blend of these exercises will contribute to your overall physical well-being, aiding in both recovery and the enhancement of your physical capabilities.
Implementation and Techniques
Proper implementation of exercise therapy hinges on careful preparation and the strategic use of equipment to meet individual needs. Your progress can be directly influenced by the frequency, intensity, and time you commit to the sessions, all while monitoring heart rate to gauge effort.
Setting and Equipment
Choosing the Right Setting: Your exercise therapy should take place in an environment that supports your well-being and energy levels. This could be a clinical setting, a gym, or even your home, as long as there is sufficient space for movement and the necessary equipment is available.
Essential Equipment: Depending on your specific goals and the prescribed technique, you might need weights, resistance bands, treadmills, or stationary bikes. Each piece of equipment is instrumental for tailoring the intensity of your workouts and is essential for varied exercise techniques aimed at improving your quality of life.
Executing Exercise Techniques
Preparation is Key: Before you start, ensure you have a clear understanding of the techniques. Preparation involves understanding the execution of each exercise, along with the desired intensity, to maximize benefits and reduce injury risk.
- Frequency: Aim to maintain a consistent routine, as dictated by your specific regimen.
- Time: Allocate enough time for each session to promote energy expenditure and well-being improvement.
Monitor Your Progress:
- Use a heart rate monitor to ensure you’re working within your target heart rate zone.
- Record your sessions to track frequency and time spent, helping you stay accountable and observe improvements.
Remember, successful exercise therapy is not just about the movements, but about the ever-improving journey towards better health and vitality.
Benefits and Outcomes
Exercise therapy is a deliberate and structured approach to using physical movement to improve your health, manage various conditions, and enhance your overall quality of life. It provides targeted benefits and can lead to significant positive outcomes for both your body and mind.
Impact on Health Conditions
Chronic Diseases: Regular therapeutic exercise is crucial for managing chronic illnesses. For example, an exercise intervention has been documented to lower the risk of diseases such as cardiovascular conditions and diabetes.
- Knee Osteoarthritis and Low Back Pain: Tailored exercise plans contribute to the management of musculoskeletal pain conditions, including knee osteoarthritis and low back pain, often reducing the disability associated with these conditions.
- Mental Health: Participation in exercise therapy can also lead to improvements in mental health issues like depression and anxiety, acting as a complement to other treatment modalities.
Physical and Psychological Advantages
- Overall Health: Engaging in therapeutic exercise promotes enhanced cardiovascular fitness, stronger muscles, better flexibility, and stability.
- Quality of Life: By reducing symptoms and improving function, exercise therapy can significantly improve your sense of well-being and quality of life.
- Recovery: Exercise therapy is often a part of rehabilitation programs, helping speed up your recovery process and return to daily activities.
Physical Fitness: By adhering to a well-designed exercise plan, you’ll likely see improvements in your physical fitness levels, contributing to better health outcomes.
RELATED READING: Hero Story: George’s Car Accident Recovery
Progress Monitoring and Adaptations
In exercise therapy, your progress is meticulously monitored to ensure you’re moving towards your health goals effectively. Adjustments are made to your program to foster improvement and manage any comorbidities or complications.
Evaluation and Feedback
Your therapy sessions will start with an evaluation of your energy levels, mobility, and range of motion to track your development. It’s crucial for you and your therapist to have open communication to discuss progress and any concerns you have. The feedback cycle is vital for:
- Identifying improvements and areas that need more focus
- Understanding the impact of any comorbidities on your exercise routine
Modifications for Improvement
Based on the feedback, adaptive techniques may be used to tailor your plan. Modifications could include:
- Altering exercise intensity or duration
- Incorporating new exercises to enhance range of motion or energy expenditure
- Adjusting for any complications to avoid injury
Your therapy personnel will guide you through these changes to ensure your safety and continual improvement.
Finding an Exercise or Physical Therapist
CWC Sport Therapy in Coquitlam BC is proud to be a leader in exercise therapy and physiotherapy. We’re dedicated to ensuring you remain active during your recovery, reducing downtime, accelerating healing, and supporting your mental well-being.